Android LinearGradient线性渐变
linearGradient线性渐变,会用到Paint的setShader,Shader 被称为着色器,在opengl中这个概念经常被用到,android中的shader主要用来给图像、文字着色,Shader在绘制过程中会返回横向重要的颜色组,Paint设置shader后,绘制时会从shader中获取颜色,也就是需要shader告诉画笔某处的颜色值。
BitmapShader,ComposeShader,LinearGradient,RadialGradient,SweepGradient
LinearGradient两种构造函数:
/**
* Create a shader that draws a linear gradient along a line.
*
* @param x0 The x-coordinate for the start of the gradient line
* @param y0 The y-coordinate for the start of the gradient line
* @param x1 The x-coordinate for the end of the gradient line
* @param y1 The y-coordinate for the end of the gradient line
* @param color0 The color at the start of the gradient line.
* @param color1 The color at the end of the gradient line.
* @param tile The Shader tiling mode
*/
public LinearGradient(float x0, float y0, float x1, float y1,
@ColorInt int color0, @ColorInt int color1, @NonNull TileMode tile) ;
/**
* Create a shader that draws a linear gradient along a line.
*
* @param x0 The x-coordinate for the start of the gradient line
* @param y0 The y-coordinate for the start of the gradient line
* @param x1 The x-coordinate for the end of the gradient line
* @param y1 The y-coordinate for the end of the gradient line
* @param colors The colors to be distributed along the gradient line
* @param positions May be null. The relative positions [0..1] of
* each corresponding color in the colors array. If this is null,
* the the colors are distributed evenly along the gradient line.
* @param tile The Shader tiling mode
*/
public LinearGradient(float x0, float y0, float x1, float y1, @NonNull @ColorInt int colors[], @Nullable float positions[], @NonNull TileMode tile) ;
参数说明: (x0,y0):渐变起始点坐标 (x1,y1):渐变结束点坐标 color0:渐变开始点颜色,16进制的颜色表示,必须要带有透明度 color1:渐变结束颜色 colors:渐变数组 positions:位置数组,position的取值范围[0,1],作用是指定某个位置的颜色值,如果传null,渐变就线性变化。 tile:用于指定控件区域大于指定的渐变区域时,空白区域的颜色填充方法。
CLAMP边缘拉伸,为被shader覆盖区域,使用shader边界颜色进行填充 -REPEAT 在水平和垂直两个方向上重复,相邻图像没有间隙 -MIRROR以镜像的方式在水平和垂直两个方向上重复,相邻图像有间隙
第一个构造函数可以指定两个颜色之间的渐变,第二个构造函数可以指定多个颜色之间的渐变,线性渐变不但可以代码实现还可以xml文件实现,这里只讲解代码实现方式。
2 两种颜色的线性渐变
只需要设置开始结束点坐标,开始颜色,结束颜色。 实例代码:
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mPaint.setTextSize(20);
LinearGradient linearGradient = new LinearGradient(getWidth(),400,0,0,Color.RED,Color.GREEN, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
mPaint.setShader(linearGradient);
canvas.drawRect(0,0,getWidth(),400,mPaint);
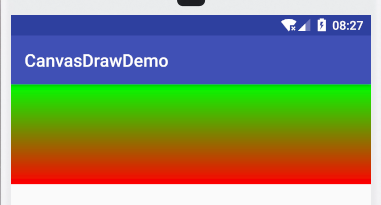
xml中设置渐变可以通过设置angle角度来改变渐变的开始结束,可以设置从上到下,从下到上,从左到右,从右到左,代码中如何设置呢?
3 如何通过坐标设置渐变方向:
通过坐标可以轻松实现,渐变方向的控制: (0,0)->(0,400)从上到下 (0,400)->(0,0) 从下到上
0,0)->(getMeasuredWidth(),0) 表示从左到右 (getMeasuredWidth(),0)->(0,0) 表示从右到左
0,0)-> (getMeasuredWidth(),getMeasuredHeight()) 斜角,从左上角到右下角
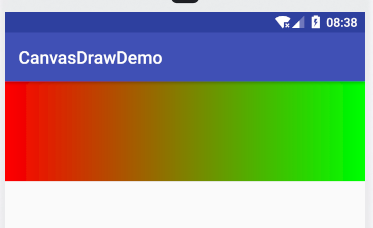
从左到右:
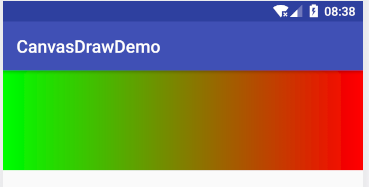
从右到左:
** 渐变填充颜色总结**
要实现从上到下需要设置shader开始结束点坐标为左上角到左下角或右上角到右下角坐标。
要实现从下到上需要设置shader开始结束点坐标为左下角到左上角或右下角到右上角。
要实现从左到右需要设置shader开始结束点坐标为左上角到右上角或者左下角到右下角。
要实现从右到左需要设置shader开始结束坐标为右上角到左上角或者右下角到左下角。
要实现对角shader,需要设置开始结束点坐标左上角到右下角。
4 多颜色填充 colors,positions数组参数讲解
LinearGradient(float x0, float y0, float x1, float y1, @NonNull @ColorInt int colors[], @Nullable float positions[], @NonNull TileMode tile) ;
positions为null时,线性填充,和没有positions数组的构造函数效果一样。
Positions数组中值为0-1,0表示开始绘制点,1表示结束点,0.5对应中间点等等。数组中位置信息对应颜色数组中的颜色。 //例如 int [] colors = {Color.RED,Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE}; float[] position = {0f, 0.3f, 1.0f}; 上面position[0]对应数组中的第一个RED,0.3f的位置对应颜色中的GREEN,1.0f的位置对应颜色中的BLUE,所以从0-0.3的位置是从RED到GREEN的渐变,从0.3到1.0的位置的颜色渐变是GREEN到BLUE。
int [] colors = {Color.RED,Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE};
float[] position = {0f, 0.3f, 1.0f};
LinearGradient linearGradient = new LinearGradient(0,0,getMeasuredWidth(),0,colors,position, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
mPaint.setShader(linearGradient);
canvas.drawRect(0,0,getMeasuredWidth(),getMeasuredHeight(),mPaint);

如果把0.3改成0.7:

5 利用LinearGradient实现变色字体
利用设置了变色shader的画笔,就可以画出变色字体:
int [] colors = {Color.RED,Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE};
float[] position = {0f, 0.7f, 1.0f};
LinearGradient linearGradient = new LinearGradient(0,0,getMeasuredWidth(),0,colors,position, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
mPaint.setShader(linearGradient);
// canvas.drawRect(0,0,getMeasuredWidth(),getMeasuredHeight(),mPaint);
canvas.drawText("Android绘图小糊涂",0,getMeasuredHeight()/2,mPaint);

如何让字体颜色不停地变动: Shader 可以设置matrix变换,利用translate不停地移动shader,实现渐变效果,下面的实例不能用于生产环境,我只是写个例子,后面会开文章讲解可用于生产的渐变。
int [] colors = {Color.BLACK,Color.RED, Color.BLUE,Color.BLACK};
Rect rect = new Rect();
mPaint.getTextBounds(str,0,str.length(), rect);
int fontWidth = rect.width();
linearGradient = new LinearGradient(0,0,-fontWidth+10,0,colors,null, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.setTranslate(tran,0);
linearGradient.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
tran = (tran + advance) ;
if (tran >= fontWidth*2){
tran = 0;
}
mPaint.setShader(linearGradient);
canvas.drawText(str,0,getMeasuredHeight()/2,mPaint);
invalidate();

TileMode 边缘填充模式
如果shader的大小小于view的大小时如何绘制其他没有被shader覆盖的区域? 跟最后一个参数有关, -CLAMP 边缘拉伸,利用边缘的颜色,填充剩余部分 -REPEAT 在水平和垂直两个方向上重复,相邻图像没有间隙,重复shader -MIRROR 以镜像的方式在水平和垂直两个方向上重复,相邻图像有间隙,镜面shader
LinearGradient linearGradient = new LinearGradient(0,0,getMeasuredWidth()/2,getMeasuredHeight()/2,Color.RED,Color.GREEN, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
mPaint.setShader(linearGradient);
canvas.drawRect(0,0,getMeasuredWidth(),getMeasuredHeight(),mPaint);
CLAMP:

REPEAT:
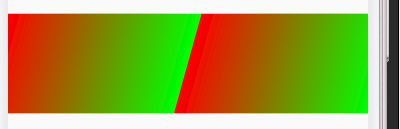
MIRROR:

如果想要从对角线设置shader,图形最好是正方形这样比较好看设置:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width =MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(width,width);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
LinearGradient linearGradient = new LinearGradient(0,0,getMeasuredWidth()/2,getMeasuredHeight()/2,Color.RED,Color.GREEN, Shader.TileMode.MIRROR);
mPaint.setShader(linearGradient);
canvas.drawRect(0,0,getMeasuredWidth(),getMeasuredHeight(),mPaint);
}